
type of pain
- sharp- Sudden, paroxysmal, varying intensity, lasting less than 1 month;
- subacute- Lasts 2-3 months, most often relapses: active for 2-5 days, then subsides, reappears some time later;
- chronic- Duration longer than one year, the course is usually recurring.
- low back pain- Pain in the lower back or lumbosacral region;
- sciatica- Located in the lower back, radiating to the legs;
- Sacroarthritis- In the sacral region;
- tailbone pain- At the tailbone.
5 facts about lower back pain
- Approximately 25% of all back pain presenting complaints are related to low back sensation.
- According to research, 84% of people experience lower back pain at least once in their lives.
- Recurrent episodes of low back pain occur in 44-78% of patients (depending on age and region of residence).
- Up to 37% of people are regularly disabled from work due to low back pain.
- Eighty-five percent of patients who consult a doctor with lower back pain are diagnosed with musculoskeletal disorders that are causing the pain.
- According to statistics, about 90% of patients with acute lumbosacral pain recover within 2 weeks.
Causes of low back pain
Musculoskeletal disorders
- Compression of the spinal roots and peripheral nerves of the lumbar spine. It occurs due to a herniated disc (degenerative change). Less commonly, it is due to hypoplasia (a disorder in the formation process) of the superior facet process of the sacrum.
- Spinal disorders caused by tumors, joint injuries, infections, compression fractures, allergic reactions, autoimmune inflammatory processes.
- Musculoskeletal disorders due to subluxations, spinal ligament sprains, muscle strains, intervertebral joint dysfunction.
internal organ pathology
- Genitourinary diseases.
Urinary tract diseases - urolithiasis, cystitis, pyelonephritis - often cause lower back discomfort. Low back pain in women may indicate reproductive organ dysfunction. In most cases, the primary sensation is concentrated in the lower abdomen and radiates to the sacrolumbar spine. They may appear during menstruation or after sexual intercourse. One possible cause of low back pain in women is ovarian tumors located on the back of the uterus. Often, lower back discomfort is a symptom of uterine fibroids. As it grows, the pain becomes intense and severe, indicating a severe disturbance in the blood supply, stretching of the peritoneum, and compression of the nerve plexus in the pelvic area. Another cause of low back pain in women is pelvic organ prolapse. In this case, the feeling has a pulling quality. Their intensity increases during walking and manual labor. - Gastrointestinal disorders.
Most commonly, pain is felt in the lower back due to gastric and duodenal ulcers and acute pancreatitis. The patient complained of pain of a surrounding nature. Typically, pain begins in the lower back and right/left ribs at the same time, where the strongest sensation is concentrated. In many clinical cases, lumbar pain accompanies the onset of acute appendicitis, although they are not the main symptom of the disease. Various inflammations of the intestinal mucosa (proctitis, sigmoiditis) can also cause pain.
10 risk factors for low back pain
- Congenital lesions of the lumbosacral spine.
- Heavy physical labor associated with lower back pressure, frequent bending, and vibration.
- Acute and chronic stress leading to muscle spasms.
- A sedentary lifestyle and being in unnatural postures for long periods of time can put a strain on the lower back.
- Weak muscles can lead to poor posture, stooping, scoliosis and kyphosis.
- Metabolic disorders and excess weight increase the load on the lower spine.
- Increased physical activity and participation in sports can increase the risk of injury.
- Age over 50 years - due to the development of degenerative processes of the spine.
- Often stressed and depressed.
- Malnutrition and lack of B vitamins.
Low back pain is a symptom of many diseases
Lumbar osteochondrosis
Symptoms of intervertebral hernia
- The patient can only rise from a seated position with the support of a chair/table or knees.
- Any load on the lower back can cause acute pain.
- The patient lies prone with only a pillow under him.
- A person can only pick up an object from the floor by squatting slowly.
ankylosing spondylitis
spondyloarthropathy
Signs of Spondyloarthropathy
- The pain worsens with exercise and disappears with rest.
- Pain occurs after standing or walking for long periods of time.
- Along with pain in the waist, the patient felt discomfort in one hip and hip joint.
urolithiasis disease
Superficial tissue and fibrous inflammation
Inflammation of spine and spinal cord
other illnesses
- Cardiovascular disease - abdominal aortic aneurysm, Loeffler endocarditis.
- Myositis is inflammation and muscle pain in the lower back that can be caused by infectious diseases like the flu, sore throat, and even the common ARVI.
- Benign and malignant tumors of the spine and spinal cord.
- Renal pathology - glomerulonephritis, renal vein thrombosis, pyelonephritis, cysts.
- Lower back pain in men is linked to prostate cancer.
Why does my lower back hurt when I cough?
- intervertebral hernia,
- osteochondrosis,
- neuralgia,
- facet joint disease,
- Kidney disease.
diagnosis
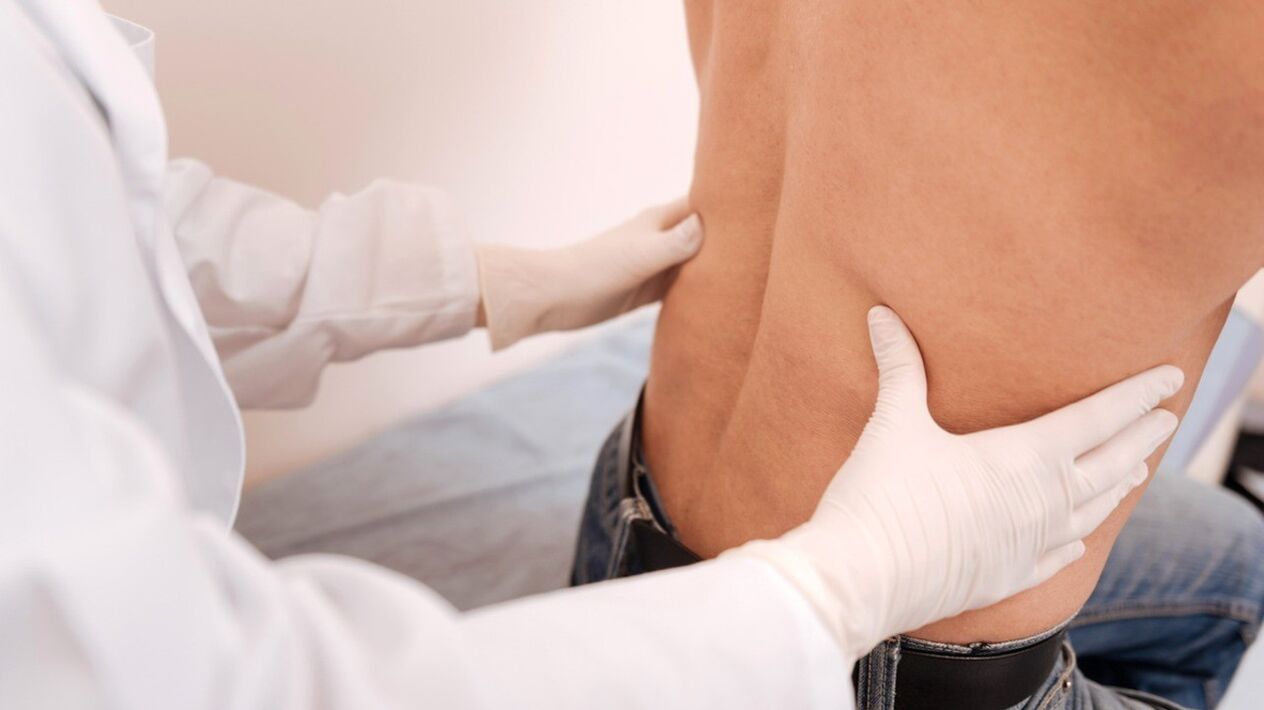
- Initial inspection.Doctors evaluate tissue sensitivity, muscle function, and reflexes in the affected area.
- Radiography.Examination shows changes in bone, cartilage, and joint structures.
- Blood and urine tests. With their help, you can determine whether there are infections and inflammatory processes.
- Functional diagnostics.It includes methods to assess nerve conduction and muscle performance - electroneurography, electromyography.
- CT and MRI.The condition of bones, muscles, nerves, and blood vessel structures can be examined in detail.
- ultrasoundThis test is done if there is suspicion of disease in the pelvic organs, prostate, or kidneys.
Is bed rest necessary?
Low back pain treatment
drug
non-drug
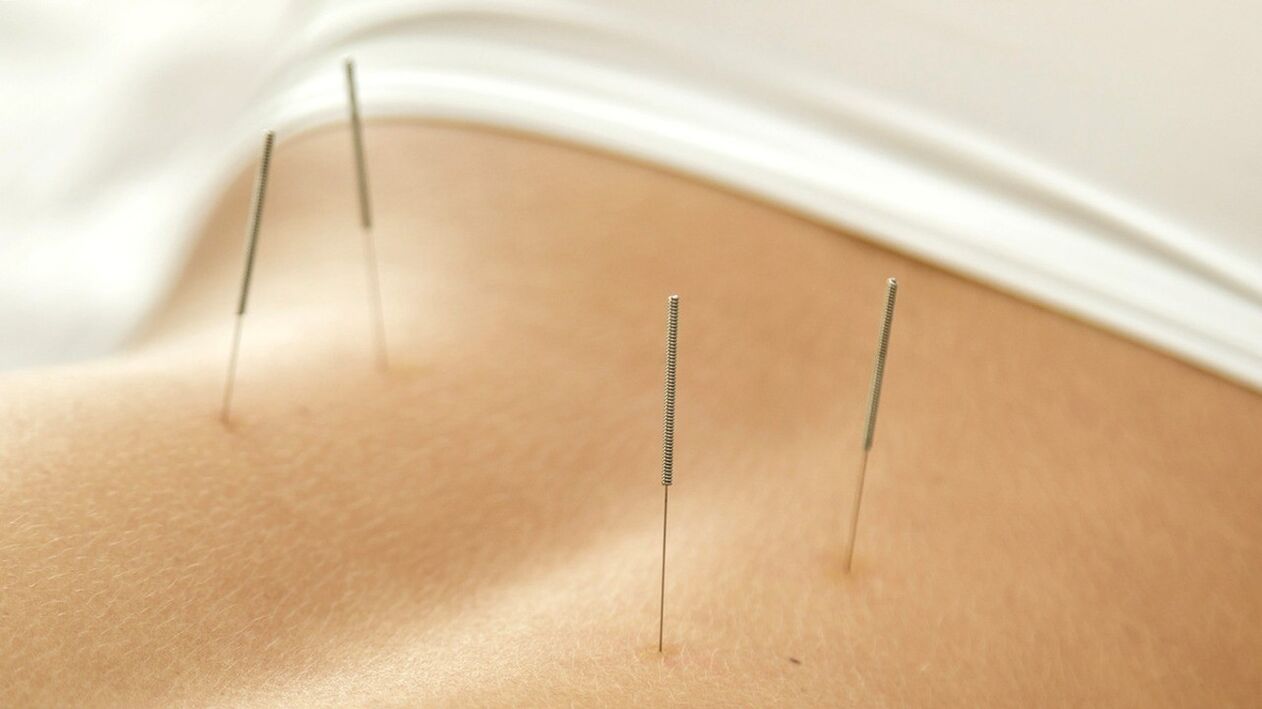
What should be done to prevent
- In the morning, perform simple spine and muscle stretches.
- Eat a reasonable diet and avoid greasy, fried, smoked, salty, spicy and alcoholic foods.
- Watch your own weight.
- Drink at least 1. 5 liters of fluid (preferably water) per day.
- Classic massage sessions every 6 months.
- Avoid staying in one position for long periods of time.
















