reason
- Thyroid disease.
- Heavy metal salt poisoning.
- Bodily harm.
- Long-term use of certain medications.
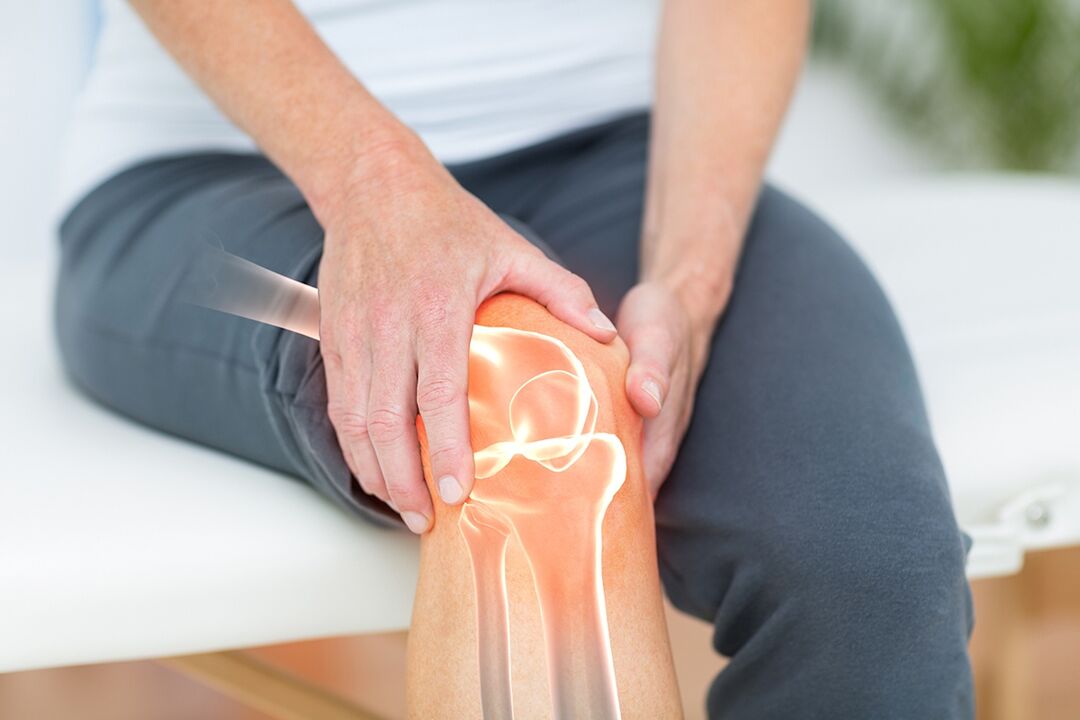
- Arthritis is an inflammatory disease of the joints caused by infection, autoimmune processes, endocrine gland and metabolic dysfunction.
- Arthropathy is a disease associated with the destruction of joint cartilage and the underlying articular surfaces of the bones. Over time, cartilage becomes rough, loses elasticity, and develops cracks.
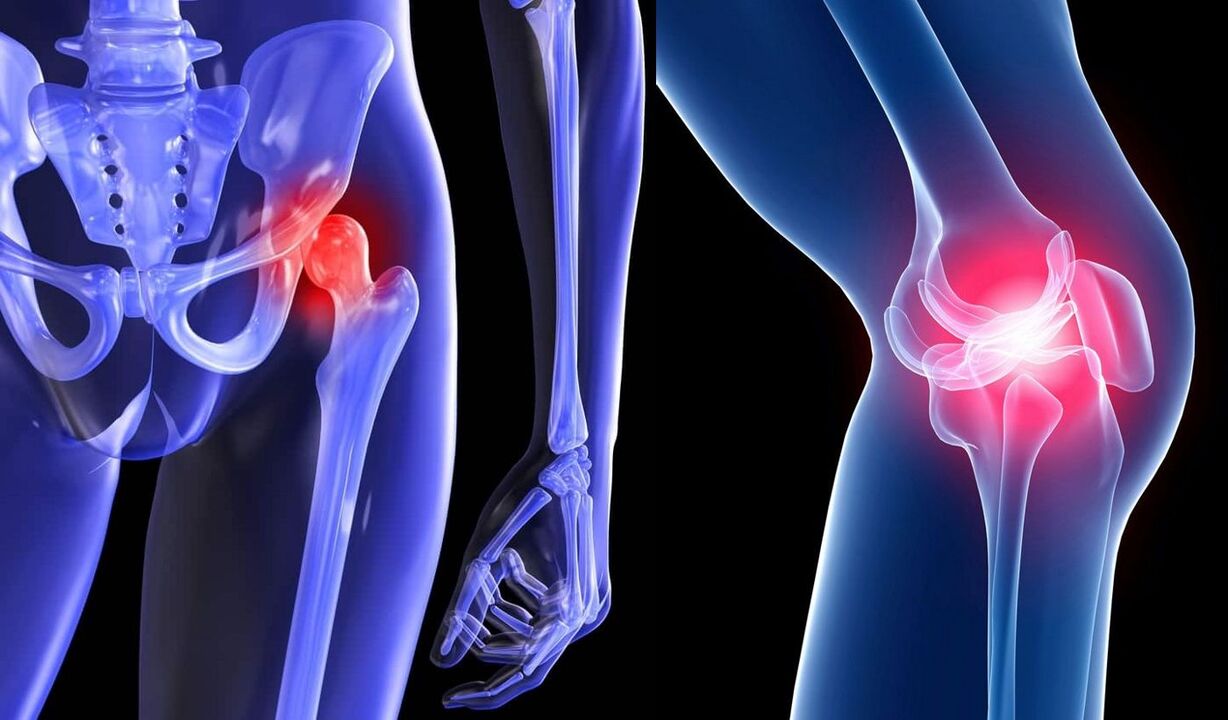
- Women during menopause.
- Older people who experience significant age-related changes in their bodies.
- Obese patients.
- Patients with a history of joint trauma.
- athlete.
- People who engage in certain professions. For example, people who stand for long periods of time (teachers, surgeons, hairdressers, etc. ) often suffer damage to their knee joints. Hand joint pain is a common symptom among musicians, cashiers, and loaders alike who perform monotonous bimanual movements.
type
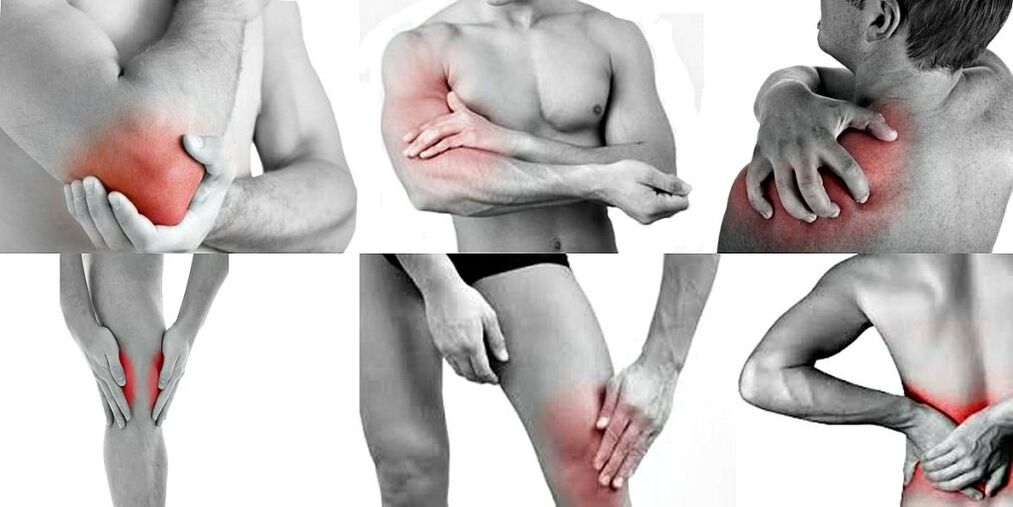
- Monarthralgia (pain in 1 joint).
- Oligoarthritis (affecting 2-5 joints).
- Polyarthralgia (pain in more than 5 joints).
- Sharp and dark.
- Temporary and permanent.
- Weak, Moderate and Strong.
- start.Joint pain occurs when you first start walking and then goes away as you move. It is related to friction on the joint surfaces of bones, which are covered with damaged cartilage tissue. After a few steps, the lump accumulates in the inversion of the joint capsule and the joint pain disappears.
- pain.They appear after physical activity in the joint and disappear after rest.
- night.They confirmed that the joints were severely damaged, caused by congestion, where blood presses against the bone tissue beneath the cartilage. After a night's sleep, the joints will feel stiff. If you move around, the discomfort will disappear.
- Everlasting.Occurs when there is inflammation of the joint capsule.
- Sudden (joint blockade). Caused by compression of a piece of bone or cartilage that is trapped between two joint surfaces.
- migrate.First there is pain in one joint, then the pain moves to another joint.
- reflect.They are felt not in the affected joint but in nearby joints. For example, if you have hip disease, you may experience pain in your knees.
diagnosis

- When pain occurs.
- The pain has since lessened and subsided.
- How often do pain attacks occur?
- Joint pain occurs for the first time or has existed previously.
- Whether the joints are congested, swollen or deformed.
- Have you had stress, acute respiratory illness, or strenuous physical activity in recent days?
- General blood and urinalysis.
- Blood Chemistry.
- Immunodiagnosis.
- Joint X-ray, CT, MRI, ultrasound.
- If necessary, a biopsy of the damaged tissue is performed.
treat
- Painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Physiotherapy (shock wave therapy, ozone therapy, muscle stimulation, phonophoresis).
- Therapeutic exercise.
- massage.
- acupuncture.
- Orthopedic or surgical correction.

- Normalize your weight.
- Wear comfortable, low-heeled shoes; if you have flat feet, use orthotic insoles.
- Avoid mental emotional and physical overload.
- While working, change your body posture frequently and spend five minutes moving to relieve muscle tension.
- To stay physically active, choose moderate exercise. Alternate activity and rest.
- Perform regular exercises to reduce stress on your joints. For example, you can sit or lie down, bend and straighten your legs for 20-30 minutes, and perform "cycling" exercises. Rest for 7-10 minutes afterwards to improve blood circulation. These exercises help strengthen the cartilage of the leg joints.
prevention

- If you are obese, normalize your weight.
- Drink at least 1. 5-1. 7 liters of water per day.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Live an active lifestyle.
- Avoid excessive drinking and smoking.
- Night sleep should last at least 8 hours.
- Take walks outdoors as often as possible.
- Try changing body positions more often.
















